60 Of 1200
interactiveleap
Sep 19, 2025 · 6 min read
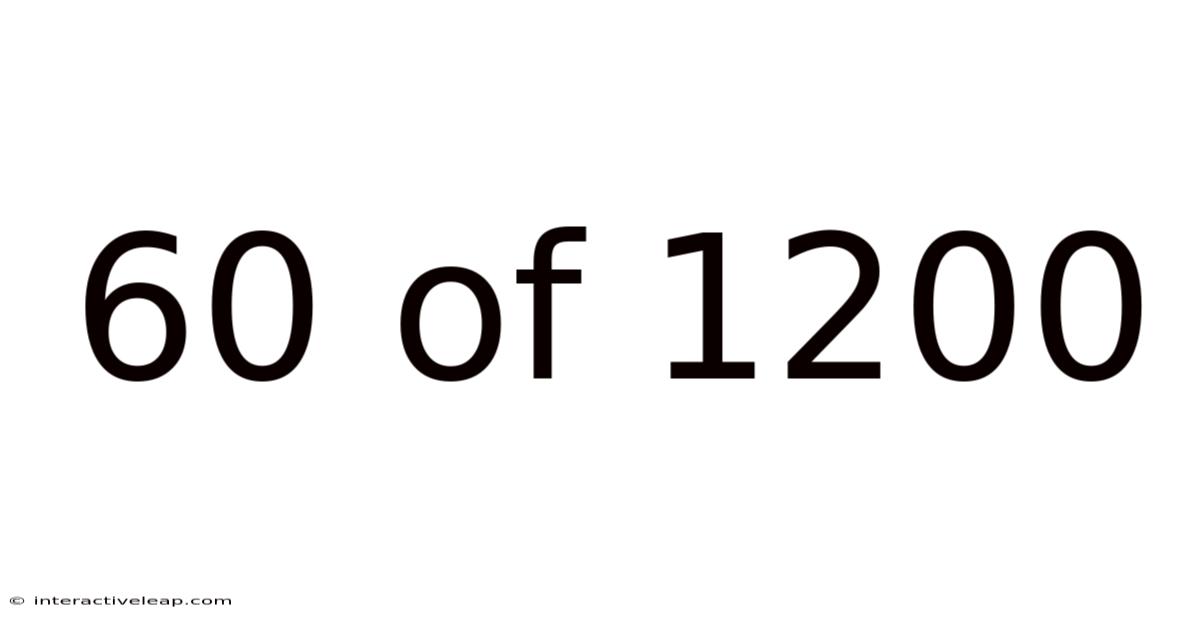
Table of Contents
Understanding 60 out of 1200: A Deep Dive into Percentages, Ratios, and Applications
This article delves into the meaning and implications of "60 out of 1200," exploring its representation as a percentage, a ratio, and its applications in various real-world scenarios. We'll move beyond a simple calculation to understand the underlying concepts and how this type of problem-solving applies to everyday life, from academic assessments to business analytics. Understanding this seemingly simple calculation opens doors to more complex mathematical concepts.
I. Calculating the Percentage:
The phrase "60 out of 1200" represents a part-to-whole relationship. To express this relationship as a percentage, we need to determine what fraction 60 represents of the total 1200 and then convert that fraction into a percentage.
The calculation is straightforward:
(60 / 1200) * 100% = 5%
Therefore, 60 out of 1200 represents 5%. This means that 60 is 5% of the total 1200. This simple percentage calculation is a cornerstone of numerous applications.
II. Understanding the Ratio:
The relationship between 60 and 1200 can also be expressed as a ratio. A ratio shows the relative size of two or more values. In this case, the ratio is 60:1200. This ratio can be simplified by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 60 and 1200, which is 60. Dividing both numbers by 60 simplifies the ratio to 1:20.
This simplified ratio, 1:20, means that for every one unit of the first value (60), there are twenty units of the second value (1200). This simplified form is crucial for understanding the proportional relationship between the two numbers and makes comparisons easier.
III. Real-World Applications:
The concept of "60 out of 1200" and its representation as a percentage or ratio has wide-ranging applications in numerous fields. Let's explore some examples:
-
Academic Performance: Imagine a student scored 60 out of 1200 possible points on a series of exams across a semester. This translates to a 5% score, indicating a significant need for improvement. Understanding this percentage allows both the student and educators to pinpoint areas needing attention and develop a targeted improvement plan. The ratio 1:20 provides a clear picture of the student's performance relative to the total possible marks.
-
Business Analytics: In a business context, 60 out of 1200 might represent the number of defective products out of a total production run. This 5% defect rate highlights the need for quality control improvements. Analyzing this data allows businesses to identify bottlenecks in the production process and implement corrective measures. The ratio provides a quantifiable measure for tracking and comparing defect rates over time.
-
Market Research: Suppose a survey of 1200 people revealed that 60 respondents preferred a particular product. The 5% preference rate helps companies understand market share and consumer preferences. This information is vital for marketing strategies and product development decisions. Again, the 1:20 ratio offers a simple, easily understandable representation of this data.
-
Healthcare: In a clinical trial involving 1200 patients, 60 patients might experience a particular side effect from a new medication. The resulting 5% incidence rate is a crucial piece of information for determining the medication's safety and efficacy. Understanding this percentage helps medical professionals evaluate the risk-benefit profile of the treatment.
-
Environmental Science: Consider a study of 1200 trees in a forest, where 60 are found to be infected with a disease. The 5% infection rate provides valuable data for understanding the spread of the disease and implementing conservation strategies. The ratio helps to visualize the proportion of affected trees compared to the total population.
IV. Expanding the Concept: Proportions and Problem Solving
The core understanding of "60 out of 1200" extends to broader concepts of proportions and problem-solving. Let's look at some examples:
-
Scaling Up: If 60 items cost $100, how much would 1200 items cost? This problem utilizes the ratio 60:100. Since 1200 is 20 times greater than 60 (1200/60 = 20), the cost of 1200 items would be 20 times the cost of 60 items: $100 * 20 = $2000.
-
Scaling Down: If a recipe calls for 1200 grams of flour and you only want to make a smaller batch using 60 grams of flour, how much of the other ingredients should you use? You would need to reduce the amount of other ingredients by a factor of 20 (1200/60 = 20).
-
Percentage Increase/Decrease: If the number of defective products increased from 60 to 120 out of 1200, what is the percentage increase? The initial defect rate was 5%. The new defect rate is (120/1200) * 100% = 10%. The percentage increase is (10% - 5%) / 5% * 100% = 100%. This means a 100% increase in the defect rate.
V. Beyond the Basics: Statistical Significance
In the context of statistics, interpreting "60 out of 1200" involves considering statistical significance. A 5% rate might seem small, but its significance depends on the context. For example, a 5% defect rate in a manufacturing process might be acceptable, while a 5% failure rate in a crucial system component could be unacceptable. Statistical tests determine whether this 5% rate is statistically significant, meaning it's unlikely to have occurred by chance. This requires further statistical analysis beyond the scope of this basic explanation.
VI. Common Errors and Misinterpretations:
-
Confusing Ratios and Percentages: While closely related, ratios and percentages represent different ways of expressing the same relationship. It's crucial to use the appropriate representation depending on the context.
-
Ignoring the Sample Size: The interpretation of "60 out of 1200" depends heavily on the total sample size (1200). A 5% rate based on a small sample size might be less reliable than a 5% rate based on a large sample size.
-
Oversimplification: While a simple percentage calculation provides a quick overview, it's vital to consider the underlying factors contributing to the observed data. A simple percentage might mask complex realities.
VII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
-
Q: How do I calculate the percentage if the numbers are different? A: Use the same formula: (part / whole) * 100%. For instance, for 80 out of 1600, the calculation is (80/1600)*100% = 5%.
-
Q: What if the "whole" number is not a whole number? A: The same principle applies. Use the formula and you'll get a percentage with decimals.
-
Q: What are some other ways to represent this data besides percentages and ratios? A: You can use fractions (60/1200 simplifies to 1/20), charts (like pie charts or bar graphs), or tables to visually represent the data.
-
Q: How do I determine if a percentage is statistically significant? A: Statistical significance testing involves using various statistical methods like hypothesis testing and confidence intervals, which are beyond the scope of this basic explanation.
VIII. Conclusion:
Understanding "60 out of 1200" involves more than just a simple calculation. It encompasses a broader understanding of percentages, ratios, proportions, and their diverse applications across various fields. By mastering these concepts, we can effectively analyze data, make informed decisions, and solve real-world problems. The seemingly simple calculation of 5% from this example is a fundamental building block for more advanced mathematical and statistical analyses, highlighting the importance of grasping even the most basic concepts. Remember that the context in which this data is presented is crucial for its accurate interpretation and application.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Hell Profanity
Sep 19, 2025
-
5 12 As Decimal
Sep 19, 2025
-
60 Of 205
Sep 19, 2025
-
Farm En Espanol
Sep 19, 2025
-
85 Of 240
Sep 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 60 Of 1200 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.