3500 / 12
interactiveleap
Sep 25, 2025 · 6 min read
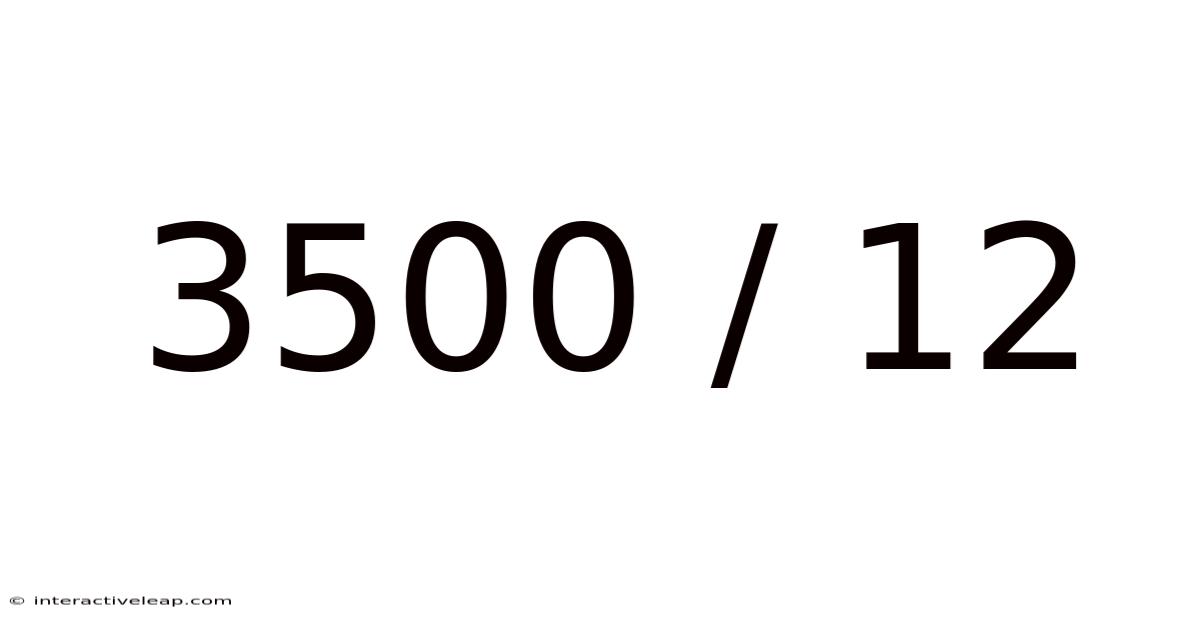
Table of Contents
Decoding 3500 / 12: A Deep Dive into Division and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple calculation of 3500 divided by 12, delving far beyond the immediate answer to uncover the underlying mathematical principles, practical applications, and various methods for solving similar problems. Understanding division is fundamental to numerous fields, from basic arithmetic to advanced engineering and finance. This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the process, enhance your mathematical intuition, and provide tools for tackling complex division problems.
Understanding Division: More Than Just Sharing
At its core, division is the process of splitting a quantity into equal parts. When we say 3500 / 12, we're asking: "If we have 3500 units, and we want to divide them into 12 equal groups, how many units will be in each group?" The number 3500 is the dividend, the number 12 is the divisor, and the result is the quotient. Sometimes, there's a remainder—a leftover amount that can't be equally distributed.
This seemingly basic operation forms the bedrock of many mathematical concepts and real-world applications. It's crucial for tasks ranging from simple budgeting and recipe scaling to complex calculations in engineering and scientific research.
Calculating 3500 / 12: Methods and Approaches
There are several ways to calculate 3500 divided by 12. Let's explore some common methods:
1. Long Division: The Classic Approach
Long division is a systematic method that breaks down the division process into manageable steps. Here's how to solve 3500 / 12 using long division:
291
12 | 3500
-24
100
-96
40
-36
4
Explanation:
- Divide: How many times does 12 go into 35? It goes 2 times (2 x 12 = 24). Write the 2 above the 5.
- Multiply: Multiply the quotient (2) by the divisor (12) to get 24.
- Subtract: Subtract 24 from 35 to get 11.
- Bring Down: Bring down the next digit (0) to make 110.
- Repeat: How many times does 12 go into 110? It goes 9 times (9 x 12 = 108). Write the 9 above the 0.
- Repeat Steps 2 & 3: Subtract 108 from 110 to get 2.
- Bring Down: Bring down the next digit (0) to make 20.
- Repeat: How many times does 12 go into 20? It goes 1 time (1 x 12 = 12). Write the 1 above the 0.
- Repeat Steps 2 & 3: Subtract 12 from 20 to get 8.
The result is a quotient of 291 with a remainder of 8. This can be expressed as 291 R 8 or 291 and 8/12, which simplifies to 291 and 2/3.
2. Using a Calculator: The Quick and Efficient Method
The simplest and fastest way to perform this calculation is to use a calculator. Simply enter "3500 ÷ 12" and the calculator will provide the answer, which is approximately 291.6667.
3. Breaking Down the Dividend: A Strategic Approach
Instead of direct long division, we can simplify the problem by breaking down the dividend (3500) into smaller, more manageable parts. For instance:
3500 = 3000 + 500
We can then divide each part separately:
3000 / 12 = 250 500 / 12 ≈ 41.67
Adding these results together gives us approximately 291.67, consistent with the other methods.
Practical Applications: Where Division Makes a Difference
The seemingly simple calculation 3500 / 12 has practical applications across numerous fields:
- Finance: Dividing a total budget among several projects or departments. For example, distributing a $3500 marketing budget across 12 different campaigns.
- Engineering: Calculating material requirements. If you need 3500 bricks to build a structure and each pallet holds 12 bricks, you’ll need 3500/12 = 291.67 pallets—round up to 292 to ensure you have enough.
- Recipe Scaling: Adjusting ingredient quantities for a larger or smaller batch. A recipe calling for 12 ounces of flour needs to be scaled up to use 3500 ounces.
- Data Analysis: Averaging data points. If you have 12 data points totaling 3500, the average is 3500/12.
- Manufacturing: Determining production rates. If a machine produces 3500 units in 12 hours, its production rate is 3500/12 units per hour.
Beyond the Numbers: Understanding Remainders and Decimal Representation
The remainder in the long division (8) represents the portion that cannot be evenly distributed among the 12 groups. This remainder can be expressed as a fraction (8/12, simplifying to 2/3) or as a decimal (0.666...). Understanding how to handle remainders is crucial for practical applications. For example, in the bricklaying example, you would need to round up to the next whole number of pallets (292) because you can't buy a fraction of a pallet. In other scenarios, the decimal representation might be more appropriate, such as when calculating average values.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The seemingly simple 3500/12 calculation opens the door to understanding more advanced mathematical concepts:
- Fractions and Decimals: The ability to convert remainders into fractions and decimals is essential for working with various types of numbers and solving real-world problems.
- Algebra: Division plays a central role in solving algebraic equations and inequalities.
- Calculus: Division is fundamental to many calculus concepts, such as derivatives and integrals.
- Statistical Analysis: Division is used extensively in statistical calculations, including calculating means, medians, and standard deviations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the exact answer to 3500 / 12?
A: The exact answer is 291 and 2/3, or 291.666... (the 6 repeats infinitely).
Q: How do I handle the remainder in a real-world problem?
A: The appropriate method depends on the context. Sometimes you need to round up to the nearest whole number (e.g., number of pallets), other times you use the decimal approximation (e.g., average value), and in some cases, the fractional representation is most useful.
Q: What are some alternative methods for solving division problems?
A: Besides long division and calculators, methods like breaking down the dividend, using estimation, or employing specialized software can be helpful.
Q: Is there a way to check my answer?
A: Yes! Multiply the quotient by the divisor and add the remainder (if any). The result should equal the dividend. For example, (291 x 12) + 8 = 3500.
Conclusion: Mastering Division for Real-World Success
The seemingly simple calculation of 3500 / 12 reveals a wealth of mathematical concepts and practical applications. By understanding the underlying principles of division, various solution methods, and the importance of handling remainders, you equip yourself with essential tools for tackling complex problems in various fields. Whether you're balancing a budget, scaling a recipe, or working on a complex engineering project, the ability to perform and interpret division accurately is invaluable. This understanding goes beyond simply finding an answer; it's about developing a deeper mathematical intuition and problem-solving prowess.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Interquartile Range Excel
Sep 25, 2025
-
15 Of 42000
Sep 25, 2025
-
Hand Vacuum Pump
Sep 25, 2025
-
Cr3 Electron Configuration
Sep 25, 2025
-
75 Of 5000
Sep 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3500 / 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.