400 X 7
interactiveleap
Sep 16, 2025 · 5 min read
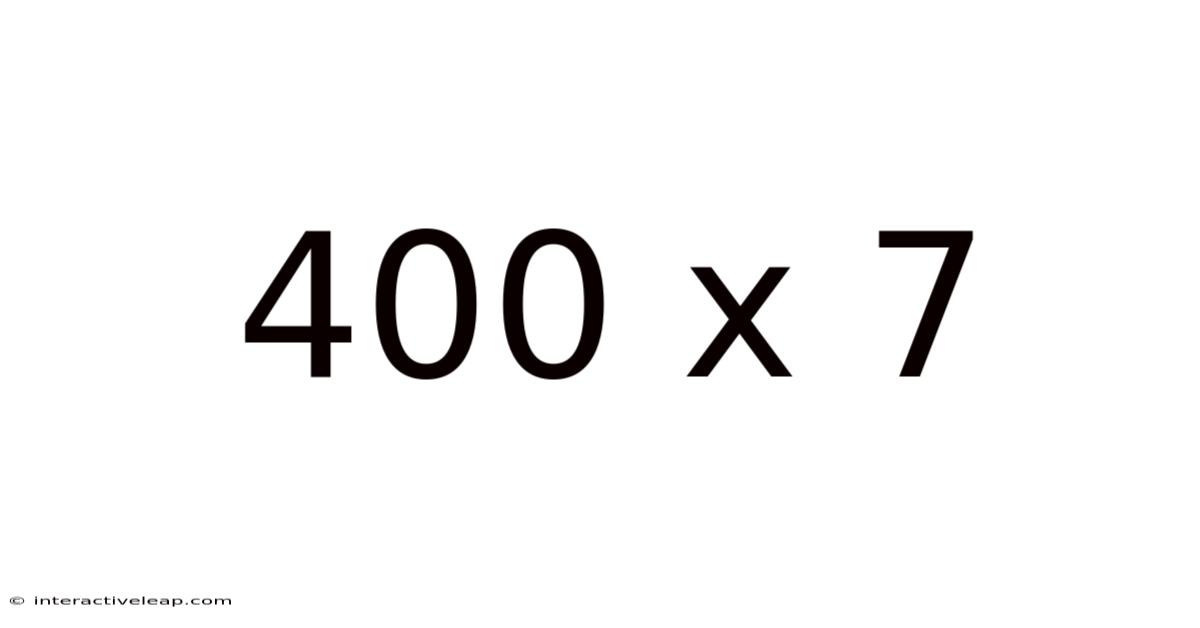
Table of Contents
Decoding 400 x 7: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
This article explores the seemingly simple multiplication problem 400 x 7, delving far beyond the immediate answer to uncover the underlying mathematical concepts, practical applications, and even the historical context of multiplication itself. Understanding this seemingly basic calculation unlocks a deeper appreciation for the building blocks of mathematics and its pervasive role in our daily lives. We’ll explore different methods of solving this problem, discuss its relevance in various fields, and address common questions surrounding multiplication.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What is Multiplication?
At its core, multiplication is repeated addition. When we say 400 x 7, we're essentially asking: "What is the sum of seven 400s?" This fundamental understanding forms the basis for all multiplication operations, regardless of the complexity. It's crucial to grasp this concept, especially when working with larger numbers. Think of it like counting groups of objects. If you have seven bags, and each bag contains 400 marbles, multiplication helps us quickly determine the total number of marbles without having to manually count each one.
Methods for Solving 400 x 7
Several approaches can be employed to solve 400 x 7. Let's explore a few:
1. Repeated Addition: The most straightforward method, as previously mentioned, is repeated addition. This involves adding 400 seven times: 400 + 400 + 400 + 400 + 400 + 400 + 400 = 2800. While effective for smaller numbers, this method becomes increasingly cumbersome as numbers grow larger.
2. Distributive Property: The distributive property of multiplication over addition allows us to break down the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. We can rewrite 400 as 4 x 100, thus transforming the problem into (4 x 100) x 7. Using the associative property, we can rearrange this as 4 x (100 x 7). Solving 100 x 7 gives us 700, and finally, 4 x 700 = 2800. This method leverages the ease of multiplying by powers of 10.
3. Standard Multiplication Algorithm: The standard algorithm, taught in most elementary schools, involves multiplying the digits place by place and carrying over values. In this case:
400
x 7
-------
2800
This method efficiently handles larger numbers, but understanding the underlying principles (repeated addition and place value) is crucial for comprehension.
4. Mental Math Techniques: With practice, mental math techniques can significantly speed up calculations. For 400 x 7, one could recognize that 4 x 7 = 28, and then simply add two zeros (representing the hundreds place in 400) to obtain 2800. This requires a good understanding of multiplication tables and place value.
Real-World Applications of Multiplication: Beyond the Textbook
The seemingly simple equation 400 x 7 has surprisingly diverse applications across various fields:
-
Business and Finance: Imagine a business selling a product for $400. If they sell seven units, the total revenue is 400 x 7 = $2800. This calculation is fundamental for determining sales, profits, and overall financial performance. Similarly, calculating salaries, stock values, and loan repayments often involves multiplication.
-
Engineering and Construction: In construction, calculating the quantity of materials needed frequently relies on multiplication. For example, if each floor of a building requires 400 bricks, and there are seven floors, a total of 2800 bricks are required. This type of calculation extends to various engineering projects involving volume, area, and other measurements.
-
Science: Scientific research often requires analyzing large datasets. Multiplication is crucial for scaling experimental results, calculating concentrations, and performing statistical analyses. If a scientist needs to repeat an experiment seven times, and each experiment uses 400 ml of a solution, they'll need a total of 2800 ml.
-
Everyday Life: Even daily activities involve multiplication. Calculating the total cost of groceries, determining the distance traveled, or figuring out the number of items needed for a project all rely on this basic arithmetic operation. Consider buying seven packs of apples at $400 per pack, the total cost is a simple application of 400 x 7.
-
Computer Science: At the heart of computer programming and algorithms, multiplication is a fundamental operation. Many computational processes rely on iterative calculations, requiring repeated multiplication for efficient computation.
The History of Multiplication: From Ancient Civilizations to Modern Calculators
The concept of multiplication has roots stretching back to ancient civilizations. Evidence suggests that multiplication techniques were developed independently in various parts of the world, reflecting the universal need for efficient counting and measurement. Ancient Egyptians used a doubling method, while Babylonian mathematicians employed a place-value system that facilitated more complex calculations. The development of multiplication algorithms evolved over centuries, eventually leading to the standardized methods we use today. The invention of the calculator further simplified the process, but understanding the underlying principles remains crucial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are some common mistakes when multiplying?
A: Common errors include incorrect place value alignment, forgetting to carry over digits, and misinterpreting the problem. Careful attention to detail and a solid understanding of the fundamentals can help prevent these mistakes.
Q: How can I improve my multiplication skills?
A: Practice is key! Regularly solving multiplication problems, using different methods, and focusing on understanding the underlying concepts will significantly enhance your skills. Memorizing multiplication tables is also helpful for quicker mental calculations.
Q: Are there other ways to represent 400 x 7?
A: Yes, 400 x 7 can also be represented as 7 x 400 (commutative property), demonstrating that the order of the numbers does not affect the outcome. It can also be represented visually using arrays or diagrams showing seven groups of 400 objects.
Q: What happens when we multiply by zero?
A: Multiplying any number by zero always results in zero. This is a fundamental property of multiplication.
Q: What about multiplying by one?
A: Multiplying any number by one results in the original number. This is the identity property of multiplication.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Multiplication
While seemingly simple, the multiplication problem 400 x 7 reveals a wealth of mathematical concepts and practical applications. From the fundamental principles of repeated addition to the sophisticated algorithms used in modern computation, understanding multiplication is essential for navigating various aspects of life, from personal finances to advanced scientific research. Mastering multiplication is not merely about finding the correct answer; it’s about grasping the underlying logic, appreciating its historical development, and recognizing its pervasive influence in our world. By understanding this seemingly basic calculation, we unlock a deeper understanding of the mathematical foundations that shape our daily experiences. This continued exploration and application will only strengthen your numerical fluency and problem-solving abilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
280 Hz Frequency
Sep 16, 2025
-
10 Of 36
Sep 16, 2025
-
75 Of 8
Sep 16, 2025
-
14 2kg In Stone
Sep 16, 2025
-
15 Off 55
Sep 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 400 X 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.