40 Of 250
interactiveleap
Sep 15, 2025 · 6 min read
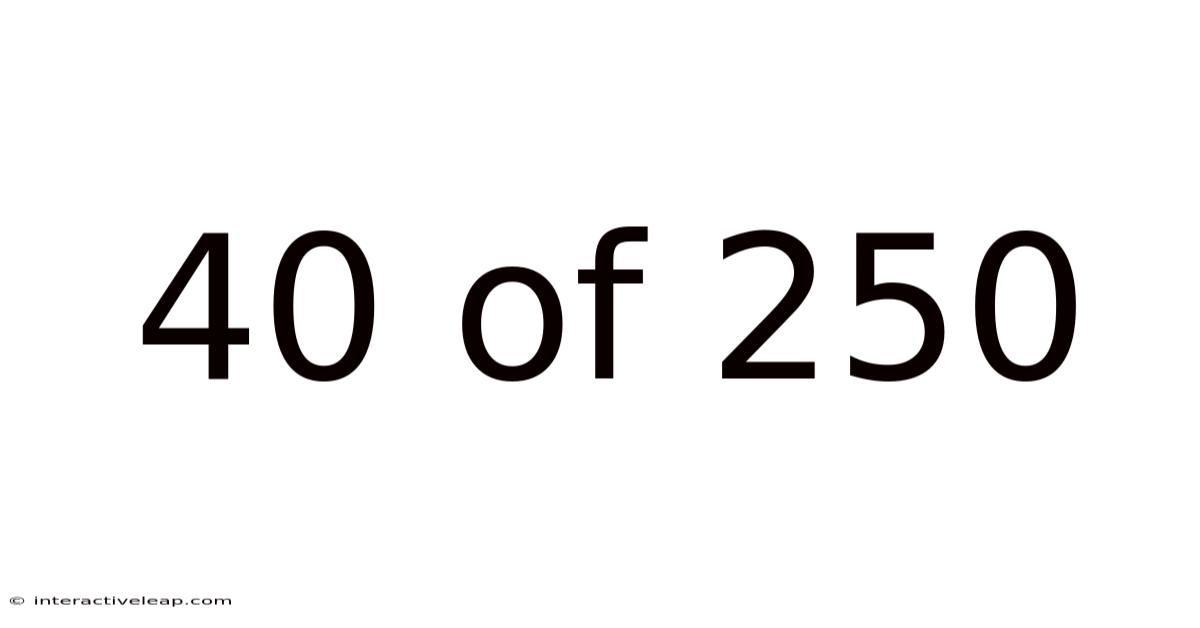
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: Understanding 40 out of 250 in Different Contexts
The phrase "40 out of 250" might seem simple at first glance, but its meaning significantly depends on the context. This seemingly straightforward ratio can represent a percentage, a fraction, a proportion within a larger dataset, or even a score in a test or game. Understanding how to interpret "40 out of 250" requires examining the specific situation and applying the appropriate mathematical tools for analysis and interpretation. This article will delve into various contexts where this ratio might appear, exploring its meaning and implications in each scenario. We’ll cover everything from simple percentage calculations to more nuanced applications in statistics and data analysis.
Understanding the Basic Calculation: Percentage and Fraction
At its core, "40 out of 250" represents a simple fraction: 40/250. This fraction can be simplified by dividing both the numerator (40) and the denominator (250) by their greatest common divisor, which is 10. This simplifies the fraction to 4/25.
To express this as a percentage, we perform the following calculation: (40/250) * 100%. This results in 16%. Therefore, 40 out of 250 represents 16%. This percentage is a crucial piece of information, providing a concise and easily understandable summary of the ratio. It's important to remember this basic calculation forms the foundation for interpreting the ratio in more complex contexts.
Contextual Applications: Where "40 out of 250" Might Appear
The interpretation of "40 out of 250" changes dramatically depending on its context. Let's explore some common scenarios:
1. Test Scores and Academic Performance
In an academic setting, "40 out of 250" could represent a student's score on a test with a total of 250 possible points. In this case, the score of 40 represents a relatively low performance, signifying a need for improvement. The percentage (16%) further emphasizes the low score. Teachers and students can use this information to identify areas needing focus and create effective learning strategies.
- Example: A student scored 40 out of 250 on a history exam. This translates to 16%, indicating a significant gap in understanding the subject matter.
2. Survey Results and Data Analysis
In surveys or polls, "40 out of 250" might represent the number of respondents who answered a particular question in a specific way. For instance, if 250 people were surveyed and 40 answered "yes" to a question, the 16% represents the proportion of respondents who gave a "yes" response. This data is valuable for understanding public opinion, consumer preferences, or market trends.
- Example: A customer satisfaction survey revealed that 40 out of 250 customers rated their experience as "poor," representing 16% dissatisfaction.
3. Quality Control and Manufacturing
In manufacturing processes, "40 out of 250" might indicate the number of defective products identified in a batch of 250. This represents a 16% defect rate. In quality control, this figure is crucial for identifying areas needing improvement in the production process to reduce defects and improve overall product quality.
- Example: A quality control check revealed 40 defective units out of 250 produced, indicating a 16% defect rate.
4. Scientific Experiments and Data Interpretation
In scientific research, "40 out of 250" could represent the number of successful trials in an experiment or the number of subjects exhibiting a particular trait. The percentage (16%) helps researchers understand the statistical significance of their findings and draw conclusions about their hypotheses.
- Example: In a clinical trial, 40 out of 250 participants showed a positive response to a new medication, suggesting a 16% effectiveness rate.
5. Sports Statistics and Performance Metrics
In sports, "40 out of 250" could represent various statistics, such as the number of successful shots, the number of points scored, or the number of successful passes. The context dictates the interpretation, but the percentage (16%) provides a quantifiable measure of performance.
- Example: A basketball player made 40 out of 250 free throws, achieving a 16% free throw percentage.
Going Beyond the Basics: Statistical Significance and Inferential Statistics
While the simple percentage calculation (16%) offers a basic understanding, a deeper analysis requires considering the broader context and employing statistical methods. This is especially important when dealing with larger datasets or when making inferences about a population based on a sample.
For instance, if "40 out of 250" represents a sample from a larger population, determining whether this 16% is statistically significant requires employing statistical tests like hypothesis testing or confidence intervals. These tests help assess whether the observed difference is likely due to chance or reflects a real difference in the population.
Addressing Potential Misinterpretations and Biases
Interpreting "40 out of 250" requires caution to avoid misinterpretations and biases. Here are some important considerations:
-
Sample Size: The size of the sample (250 in this case) affects the reliability of the results. Larger sample sizes generally lead to more reliable estimates.
-
Sampling Bias: If the sample is not representative of the population, the results may be biased and not generalize to the larger population.
-
Contextual Factors: Always consider the specific context in which the ratio is presented. The same ratio can have vastly different meanings depending on the situation.
-
Correlation vs. Causation: Just because two variables are correlated does not mean that one causes the other. Statistical analysis can help determine the strength and direction of the relationship, but further investigation might be needed to establish causality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do I calculate the percentage from "40 out of 250"?
A: Divide 40 by 250 and then multiply by 100%. (40/250) * 100% = 16%
Q: What if the numbers were different? How would I calculate the percentage for other ratios?
A: The same formula applies: (Part/Whole) * 100%. Replace "Part" with the smaller number and "Whole" with the larger number.
Q: Is 16% a good or bad percentage?
A: The interpretation of 16% depends entirely on the context. In some situations, 16% might be considered excellent, while in others, it might be very poor.
Q: What statistical tests could be used to analyze data related to this ratio?
A: Depending on the specific research question and data type, various statistical tests could be used, including t-tests, chi-square tests, ANOVA, and others.
Q: How can I ensure my data analysis is free from bias?
A: Employ rigorous sampling methods to ensure your sample is representative of the population. Carefully consider potential confounding factors and biases that might influence the results. Transparency in data collection and analysis methods is crucial.
Conclusion: The Importance of Context and Critical Thinking
The seemingly simple ratio "40 out of 250" demonstrates the crucial role of context in data interpretation. While the basic percentage calculation provides a starting point, a deeper understanding requires considering the specific context, employing appropriate statistical tools, and critically evaluating potential biases. Remember to always consider the bigger picture and avoid simplistic interpretations without a thorough understanding of the underlying situation. The ability to correctly interpret such ratios is a valuable skill applicable across diverse fields, emphasizing the importance of numerical literacy and critical thinking in our data-driven world. By mastering these analytical skills, we can derive meaningful insights from data and make informed decisions based on accurate interpretations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
22 99 X 12
Sep 15, 2025
-
Best Detangling Brush
Sep 15, 2025
-
48f In C
Sep 15, 2025
-
Electrical Sewing Machine
Sep 15, 2025
-
11 5cm In Inches
Sep 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 40 Of 250 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.