30 Of 320
interactiveleap
Sep 24, 2025 · 6 min read
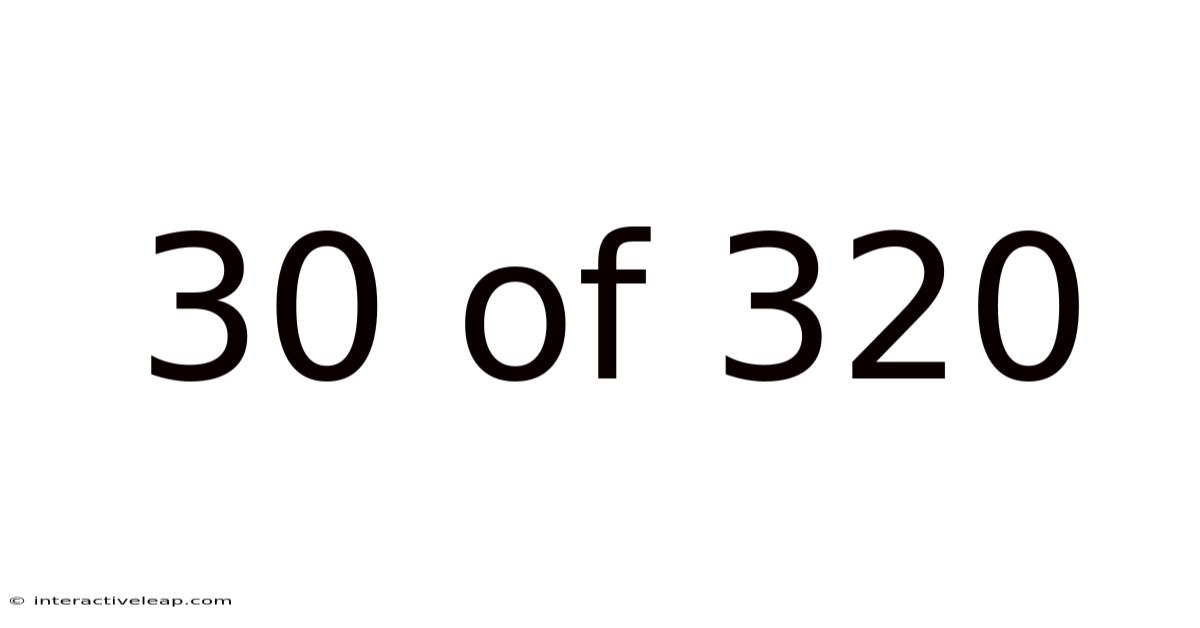
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Understanding the Significance of "30 of 320"
The phrase "30 of 320" might seem innocuous at first glance, a simple numerical expression. However, depending on the context, it can represent a powerful data point, a progress indicator, or even a symbol of achievement. This article delves into the various interpretations and applications of this seemingly simple fraction, exploring its significance across different fields and providing a framework for understanding its implications. We'll explore how understanding this type of data can help you make better decisions and interpret information more effectively.
Understanding the Fraction: 30/320
At its most basic level, "30 of 320" represents a fraction: 30/320. This fraction can be simplified to 3/32 by dividing both the numerator (30) and the denominator (320) by 10. This simplification helps visualize the proportion more clearly. The fraction indicates that 30 represents a portion of a larger whole, 320. This larger whole could represent anything, from a total number of tasks, to a quantity of items, or even a statistical sample size.
The key to understanding the significance of "30 of 320" lies in determining what the 320 represents. Once we know the context, we can accurately interpret the meaning and implications of the 30.
Context is King: Interpreting "30 of 320" in Different Scenarios
The interpretation of "30 of 320" drastically changes based on its context. Let's examine several potential scenarios:
1. Project Management & Task Completion:
Imagine a project with 320 individual tasks. "30 of 320" would indicate that 30 tasks have been completed, leaving 290 tasks outstanding. This represents approximately 9.4% completion (30/320 * 100%). In this context, the data point provides crucial insight into project progress. It can be used to:
- Monitor progress: Tracking the number of completed tasks against the total helps maintain project momentum.
- Identify bottlenecks: If progress is slower than expected, analyzing which tasks remain can highlight bottlenecks.
- Adjust timelines: Based on current progress, project timelines can be adjusted to reflect reality.
- Allocate resources: Resource allocation can be optimized based on the remaining tasks and their urgency.
2. Sales and Marketing Performance:
In a sales context, 320 might represent the total number of leads generated during a campaign. "30 of 320" would then mean that 30 leads have converted into sales. This 9.4% conversion rate can be analyzed against previous campaigns to assess performance. This data can:
- Measure campaign effectiveness: A low conversion rate might indicate a need for campaign adjustments.
- Inform future strategies: Understanding what worked (or didn't) with the 30 successful conversions can inform future marketing strategies.
- Optimize resource allocation: Resources can be shifted towards more effective lead generation or conversion strategies.
3. Statistical Analysis & Sampling:
In statistical research, 320 might be the size of a sample population. "30 of 320" could then represent the number of participants exhibiting a specific characteristic within that sample. This provides a measure of prevalence or incidence. For instance:
- Medical research: If 320 patients are studied, and 30 exhibit a specific symptom, this provides data on the symptom's prevalence within the studied population.
- Social science research: Similar applications can be found in social science research, where "30 of 320" might represent a specific demographic or response to a survey.
4. Inventory Management:
In a warehouse or inventory management setting, 320 might signify the total number of a specific product. "30 of 320" would indicate that 30 units have been sold or shipped. This data point is essential for:
- Demand forecasting: Understanding the rate of sales helps predict future demand.
- Inventory control: It informs restocking strategies, preventing stockouts or overstocking.
- Optimizing storage: Efficient storage strategies can be implemented based on sales data and demand.
5. Manufacturing & Production:
In a manufacturing setting, 320 could represent the total number of units produced in a batch. "30 of 320" might then indicate the number of defective units. This information is critical for:
- Quality control: High numbers of defective units can signal issues in the production process.
- Process improvement: Analyzing the defects can identify areas for process improvement to reduce waste and improve quality.
Beyond the Numbers: The Importance of Contextual Analysis
The examples above highlight the crucial role of context in interpreting "30 of 320." Simply stating the fraction provides minimal information. To derive meaningful insights, we must understand what the numbers represent within their specific context. This necessitates careful consideration of the larger system or process involved.
Extending the Analysis: Further Considerations
Beyond simply calculating the percentage (9.4% in our example), a deeper analysis requires considering various factors:
- Trend Analysis: Is "30 of 320" an improvement or decline compared to previous periods? Tracking this data over time provides crucial insights into trends and patterns.
- Benchmarking: How does "30 of 320" compare to industry benchmarks or competitor performance? This comparison provides valuable context for evaluating success.
- Causality: What factors contributed to the "30 of 320" result? Identifying causal factors allows for more informed decision-making.
- Data Quality: Is the data accurate and reliable? Errors in data collection can skew interpretations.
- Uncertainty: What level of uncertainty is associated with "30 of 320"? Statistical methods can help quantify this uncertainty.
Applying this Knowledge: Practical Examples
Let's consider a few practical examples to solidify the understanding:
Example 1: A marketing campaign resulted in 30 conversions out of 320 leads. This represents a 9.4% conversion rate. However, the campaign's budget was significantly higher than anticipated. This information is crucial – a low ROI despite a seemingly acceptable conversion rate suggests adjustments to the campaign strategy or budget allocation are needed.
Example 2: A manufacturing process produced 320 units, with 30 being defective. A seemingly low defect rate might be acceptable, but if it represents a significant increase compared to previous batches, it signals a potential issue within the production process. This requires immediate investigation and corrective action.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do I calculate the percentage represented by "30 of 320"?
A: Divide the numerator (30) by the denominator (320) and multiply the result by 100 to obtain the percentage: (30/320) * 100 = 9.375% ≈ 9.4%.
Q: What if the "320" figure changes? How does that affect the interpretation?
A: A change in the denominator (320) significantly alters the interpretation. For example, if the total number increases to 640, then 30/640 represents a much lower proportion (4.7%). Conversely, if it decreases, the proportion increases.
Q: Are there any tools or software that can help analyze this type of data?
A: Yes, various spreadsheet software (like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets), statistical software packages (like SPSS or R), and project management software offer tools to track, analyze, and visualize this type of data.
Conclusion: The Power of Contextual Understanding
The seemingly simple expression "30 of 320" holds significant meaning when considered within its specific context. It's not just a fraction; it’s a data point that can offer critical insights into project progress, sales performance, statistical analysis, and numerous other applications. The ability to understand and analyze such data points is fundamental for effective decision-making across various fields. Remember, always consider the context, analyze trends, and look for underlying causes to extract the full value of this type of data. The more context you bring to the analysis, the richer your understanding of the information will be.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
44f In Celsius
Sep 24, 2025
-
78 In Cm
Sep 24, 2025
-
The Shuffle Deck
Sep 24, 2025
-
3n Squared Sequence
Sep 24, 2025
-
Bone Apple Tea
Sep 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 30 Of 320 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.