20 Of 460
interactiveleap
Sep 15, 2025 · 7 min read
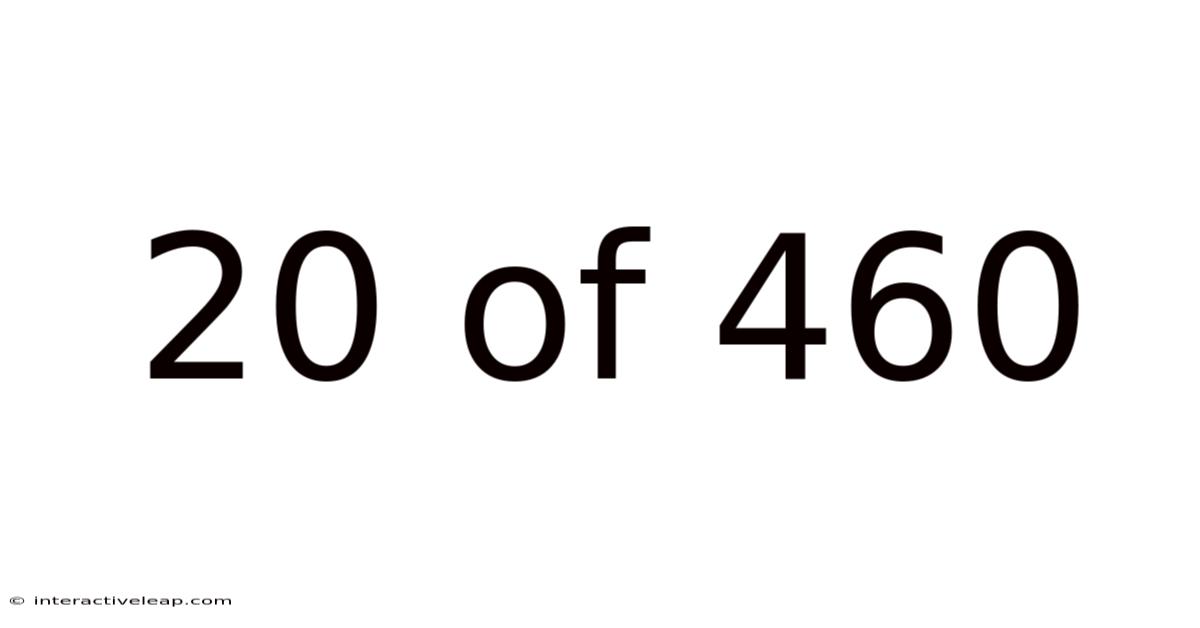
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: Understanding the Significance of 20 out of 460
The seemingly simple fraction, 20 out of 460, holds a surprising depth of meaning depending on the context. This article will explore the various interpretations and applications of this ratio, from basic percentage calculations to its implications in statistical analysis, probability, and even everyday scenarios. We'll delve into the practical methods for calculating its significance and examine how understanding this ratio can improve problem-solving skills across various disciplines.
Introduction: The Power of Proportions
Understanding proportions is fundamental to many aspects of life. Whether it's calculating discounts, analyzing survey results, or understanding the performance of a sports team, the ability to interpret ratios is crucial. The ratio 20 out of 460, or 20/460, is a prime example of how a seemingly small fraction can carry significant weight depending on the situation. This article will unpack this ratio, exploring its calculation, interpretation, and practical applications. We'll cover everything from the basics of percentage calculation to more advanced statistical concepts, ensuring that readers of all levels can grasp the importance of understanding proportions like 20/460.
Calculating the Percentage: A Simple Approach
The most straightforward way to understand 20 out of 460 is by calculating its percentage. This involves dividing the smaller number (20) by the larger number (460) and then multiplying the result by 100.
- Calculation: (20 / 460) * 100 = 4.35% (approximately)
This tells us that 20 represents approximately 4.35% of 460. This simple calculation provides a concise way to understand the relative proportion of 20 within the larger whole of 460. This percentage representation is easily understood and communicated, making it a valuable tool for conveying information quickly and effectively.
Beyond the Percentage: Exploring Statistical Significance
While the percentage provides a clear overview, understanding the statistical significance of 20 out of 460 requires further analysis. The significance depends heavily on the context. For example:
-
In a survey: If 20 out of 460 respondents answered "yes" to a particular question, this 4.35% might be considered statistically insignificant if the margin of error is high. However, in a smaller survey, this could represent a more substantial finding.
-
In a medical trial: If 20 out of 460 patients experienced a side effect from a new drug, this relatively small percentage still needs careful consideration. Further analysis would be crucial to determine if this side effect is genuinely linked to the drug or simply a random occurrence.
-
In quality control: If 20 out of 460 manufactured items are defective, this represents a 4.35% defect rate. Depending on industry standards, this rate might be acceptable, or it might signal a need for improvements in the manufacturing process.
Applications in Various Fields
The interpretation of 20/460 varies significantly across different disciplines:
-
Business and Finance: This ratio could represent market share, customer satisfaction rates, or investment returns. The interpretation would hinge on the specific context and industry benchmarks.
-
Education: In a classroom setting, 20 out of 460 students achieving a specific grade could reveal insights into teaching methods or student learning outcomes.
-
Science: In scientific research, this ratio could represent the success rate of an experiment, the prevalence of a specific phenomenon, or the proportion of a certain element in a compound.
-
Sports: This ratio could reflect a player's success rate (e.g., 20 successful shots out of 460 attempts), the win-loss ratio of a team, or various other performance metrics.
Probability and Risk Assessment
The ratio 20/460 can also be used in probability calculations. For instance, if 20 out of 460 events resulted in a specific outcome, the probability of that outcome occurring in a future event can be estimated at approximately 4.35%. However, this is a simplistic approach and more sophisticated statistical models might be required for more accurate probability estimations, especially when dealing with complex scenarios.
Understanding Confidence Intervals
When interpreting 20 out of 460, especially in statistical studies, it's essential to consider confidence intervals. A confidence interval provides a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to fall with a certain level of confidence (e.g., 95%). A smaller sample size (like 460 in this case) generally leads to wider confidence intervals, indicating greater uncertainty in the estimation. Calculating confidence intervals is crucial for assessing the reliability of the 4.35% figure obtained from the 20/460 ratio.
The Importance of Sample Size
The sample size of 460 plays a vital role in interpreting the significance of the 20 successes. A larger sample size generally leads to more reliable results and narrower confidence intervals. Conversely, a smaller sample size, while still offering valuable data, comes with greater uncertainty. Thus, the interpretation of 20/460 must always consider the sample size to accurately assess the findings.
Practical Example: Analyzing Survey Results
Let's consider a hypothetical example: A survey on customer satisfaction was conducted, and 20 out of 460 respondents rated their satisfaction as "poor." While the 4.35% seems low, we need more context.
- What is the margin of error? A larger margin of error reduces the certainty of the result.
- What is the demographic breakdown of respondents? The percentage might be higher or lower within specific demographic groups.
- What actions can be taken based on this data? This low percentage might still warrant investigation to understand the root causes of the dissatisfaction.
This example illustrates that simply calculating the percentage isn't enough; further analysis and contextual understanding are crucial for proper interpretation.
Addressing Potential Biases
It's critical to consider potential biases that could affect the interpretation of 20/460. Biases can skew the results, leading to inaccurate conclusions. For example:
- Sampling bias: The 460 respondents might not represent the entire population accurately.
- Response bias: Respondents might not answer honestly or accurately.
- Measurement bias: The method used to collect the data might introduce errors.
Addressing these potential biases is crucial for ensuring the reliability and validity of the findings. This often involves careful survey design, rigorous data collection methods, and statistically sound analysis techniques.
Advanced Statistical Techniques
For a more in-depth analysis of the 20/460 ratio, advanced statistical techniques such as hypothesis testing and regression analysis might be employed. These techniques can help to determine whether the observed proportion is statistically significant or simply due to chance. Such analyses are typically performed using statistical software packages and often involve sophisticated calculations beyond the scope of a basic percentage calculation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How can I calculate the percentage of 20 out of 460 using a calculator?
A1: Simply divide 20 by 460, then multiply the result by 100. Most calculators will perform this calculation directly.
Q2: Is a 4.35% result statistically significant?
A2: The statistical significance depends entirely on the context. A larger sample size generally leads to more reliable results and increases the likelihood of statistical significance.
Q3: What if the numbers were different, say 200 out of 460? How would that change the interpretation?
A3: 200 out of 460 represents a much larger proportion (approximately 43.5%), significantly altering the interpretation and potentially leading to very different conclusions depending on the context.
Q4: What are some examples of real-world scenarios where this kind of ratio analysis is used?
A4: Examples include analyzing customer satisfaction scores, calculating defect rates in manufacturing, determining the efficacy of medical treatments, assessing election results, and many others.
Q5: Are there any online tools to help with this type of calculation?
A5: While dedicated tools for specifically this ratio are unnecessary, many online calculators and statistical software packages can handle percentage calculations, confidence interval estimations, and other relevant statistical analyses.
Conclusion: Context is King
In conclusion, the seemingly simple ratio of 20 out of 460, while easily converted to a percentage (approximately 4.35%), offers much more than a single numerical value. Its significance is heavily context-dependent. Understanding the nuances of statistical analysis, considering sample size, acknowledging potential biases, and applying relevant statistical methods are all crucial for interpreting this ratio accurately and making informed decisions based on the data. Remember, context is paramount when dealing with proportions and statistical analyses. The number itself is only a starting point for a deeper, more insightful understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
80 8kg In Stone
Sep 15, 2025
-
98 9f To C
Sep 15, 2025
-
7 2 As Fraction
Sep 15, 2025
-
Sales Forecast Example
Sep 15, 2025
-
1 65 Kg Pounds
Sep 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 20 Of 460 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.