2 X 128
interactiveleap
Sep 17, 2025 · 7 min read
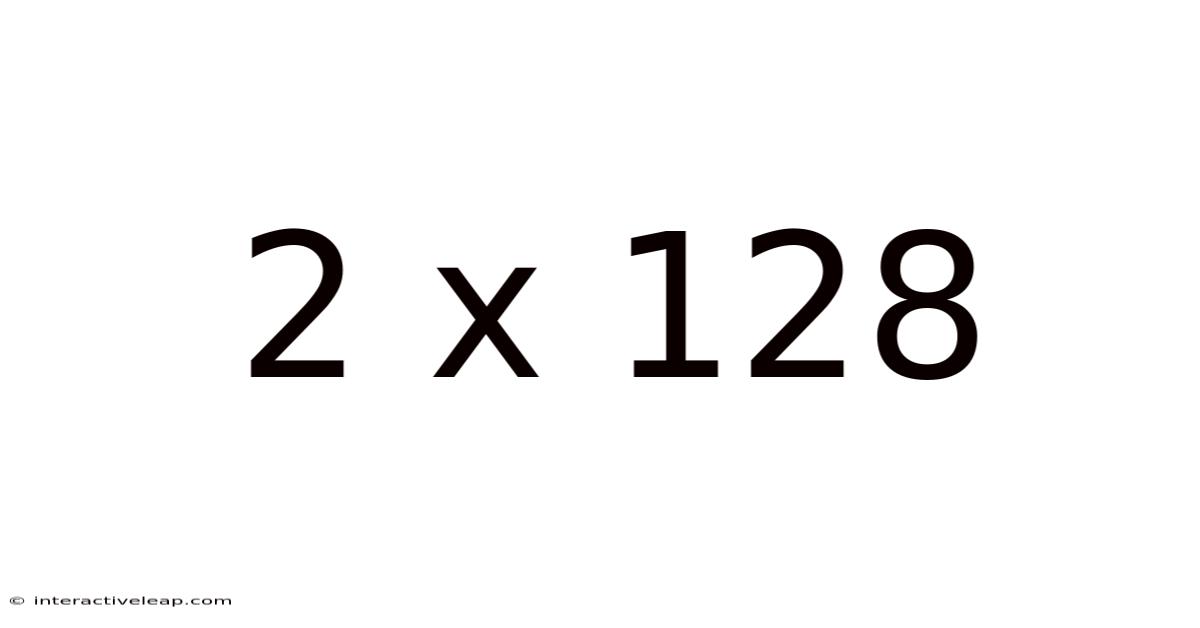
Table of Contents
Decoding 2 x 128: Understanding Memory, Data, and Parallel Processing
The seemingly simple expression "2 x 128" can represent a surprisingly diverse range of concepts, depending on the context. This article delves into the multifaceted meaning of this expression, exploring its implications in memory organization, data representation, parallel processing, and more. We'll unravel its significance across various fields, from computer science and engineering to mathematics and even music. Understanding "2 x 128" allows us to appreciate the fundamental building blocks of many complex systems.
Introduction: The Ubiquity of 2 x 128
At its most basic, "2 x 128" signifies a simple multiplication: 2 multiplied by 128 equals 256. However, its meaning extends far beyond this elementary calculation. In the world of computing and data processing, this expression often refers to the arrangement and organization of data. It could indicate:
- Memory organization: Two memory banks, each with a capacity of 128 units (bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, etc.).
- Data structures: Two arrays, each containing 128 elements.
- Parallel processing: Two processors or threads concurrently processing 128 units of data.
- Signal processing: Two channels each sampling at a rate of 128 Hz.
This article will systematically explore each of these interpretations, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of how "2 x 128" manifests itself in various applications.
2 x 128 in Memory Organization and Data Structures
In computer architecture, "2 x 128" might describe a memory system's configuration. Imagine a system with two separate memory modules, each capable of holding 128 megabytes (MB) of data. This dual-channel memory setup offers performance advantages, allowing the system to fetch data from both modules simultaneously, significantly boosting data throughput. This is particularly relevant in tasks that require extensive data access, such as video editing, 3D rendering, and scientific simulations.
Similarly, in programming, "2 x 128" can represent data structures. For instance, a programmer might define two arrays, each containing 128 elements. These arrays could store anything from numerical data to strings or more complex objects. The choice of using two separate arrays instead of one large array might be dictated by factors like code clarity, memory management strategies, or the specific requirements of the algorithm being implemented. This division can improve code readability and potentially optimize memory access patterns.
Consider a scenario involving the processing of sensor data. Each sensor might provide 128 data points per second. Using two sensors means a total of 256 data points per second which needs to be processed efficiently. The "2 x 128" structure directly reflects this data inflow, allowing for straightforward organization and parallel processing of the sensor information.
Parallel Processing and Concurrency with 2 x 128
The concept of parallel processing is central to modern computing. "2 x 128" could describe a system where two processors or cores are each responsible for processing 128 units of data concurrently. This approach drastically reduces processing time compared to sequential processing, where a single processor would handle all 256 units one after another. This is fundamental to high-performance computing, enabling tasks that would be intractable on single-processor systems.
This parallel approach is used extensively in image and video processing. Imagine processing a large image. Instead of processing the entire image on a single core, the image can be divided into two halves (128 pixels each), with each core independently processing its assigned portion. The results are then combined to produce the final processed image, significantly speeding up the entire process. Similar techniques are used in scientific simulations, financial modeling, and machine learning algorithms.
The efficiency of parallel processing hinges on effective data distribution and communication between the processors. In the "2 x 128" example, minimizing data transfer overhead between the two processors is crucial for achieving optimal performance. This requires careful consideration of data structures, algorithms, and hardware architecture.
2 x 128 in Signal Processing and Audio Engineering
In the realm of audio engineering and signal processing, "2 x 128" might refer to a system with two audio channels, each sampling at a rate of 128 Hz. The sampling rate determines how many data points are captured per second, representing the fidelity of the audio signal. While 128 Hz is a relatively low sampling rate, this example illustrates the application of this notation in specifying audio parameters. Higher sampling rates (e.g., 44.1 kHz for CD quality audio) are common, but the "2 x 128" format clarifies the channel configuration and the sampling rate for each channel.
This concept extends to other types of signal processing, such as sensor data acquisition. Two sensors might each transmit 128 data points per second, representing different physical quantities. The "2 x 128" representation provides a concise way to describe the data stream configuration. Efficient processing of this data requires strategies that handle the parallel input from both sensors while ensuring data synchronization and integrity.
Mathematical Interpretations and Beyond
While the focus has been on computer science and engineering applications, "2 x 128" also holds mathematical relevance. It's a simple multiplication problem, but it can be part of more complex equations or algorithms. For instance, it could represent a coefficient in a linear equation or a dimension in a matrix operation. The specific meaning would be defined by the broader mathematical context.
Beyond the technical applications, "2 x 128" could even have less conventional interpretations. In music, for example, it might refer to a musical composition with two sections, each containing 128 bars or measures. This is a less common interpretation, illustrating that the numerical representation's meaning is heavily context-dependent.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the significance of the number 128?
A: The number 128 is a power of 2 (2<sup>7</sup>). Powers of 2 are frequently used in computing because they align well with binary representations and memory addressing. The use of 128 often reflects the underlying binary structure of computer systems.
Q: Are there performance differences between a 2 x 128 setup and a single 256 system?
A: In many cases, a 2 x 128 setup can offer performance advantages due to parallel processing capabilities. However, the actual performance gain depends on the specific hardware, software, and the nature of the task being performed. If the task is not easily parallelizable, a single 256 system might be equally efficient or even faster.
Q: What are some potential limitations of using a 2 x 128 structure?
A: Potential limitations include increased complexity in managing data across multiple channels or memory modules. Data synchronization and communication overhead between the two units can become significant bottlenecks if not handled efficiently. Also, the cost of hardware with a 2 x 128 structure might be slightly higher compared to a single-unit equivalent.
Q: Can "2 x 128" represent other things besides memory and data?
A: Yes, absolutely. The expression's meaning is entirely context-dependent. It could signify dimensions in geometry, a quantity of items in a batch process, or even a musical structure. The interpretation depends on the specific application or field.
Conclusion: The Expanding Meaning of 2 x 128
"2 x 128" is more than just a simple mathematical expression. Its meaning expands significantly within the context of computing, data processing, and signal processing. This article has explored its implications in memory organization, data structures, parallel processing, and audio engineering. The seemingly simple phrase illuminates fundamental concepts at the heart of modern technology, underscoring the importance of understanding how data is organized and processed in complex systems. By understanding its various interpretations, we gain a deeper appreciation of the underlying principles that govern the digital world around us. The versatility of this simple expression highlights the fundamental role of numerical representation in shaping the functionality and performance of technological systems. Further investigation into the specific context surrounding its use is always necessary for accurate and complete interpretation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
77 X 2
Sep 17, 2025
-
1 5 Scale
Sep 17, 2025
-
220c To F
Sep 17, 2025
-
30 Of 260
Sep 17, 2025
-
57 1kg In Stone
Sep 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 X 128 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.