15 Of 1600
interactiveleap
Sep 17, 2025 · 5 min read
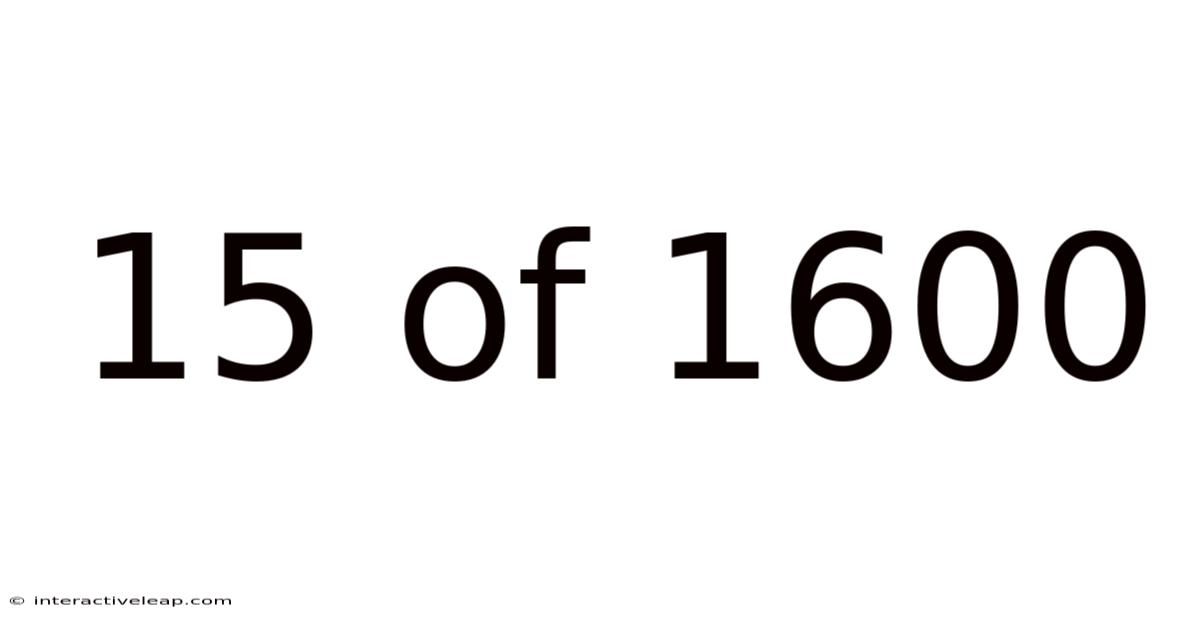
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Enigma: 15 out of 1600 – A Deep Dive into Percentages, Probabilities, and Real-World Applications
Understanding fractions, percentages, and probabilities is fundamental to navigating the complexities of the world around us. This article delves into the seemingly simple yet powerfully illustrative example of "15 out of 1600," exploring its meaning, calculations, implications, and practical applications across various fields. We'll move beyond simple percentage calculations to explore the underlying statistical concepts and demonstrate how this seemingly small fraction can hold significant meaning depending on the context.
Understanding the Basics: Fractions, Percentages, and Ratios
Before we dive into the specifics of 15 out of 1600, let's refresh our understanding of fundamental mathematical concepts.
-
Fraction: A fraction represents a part of a whole. In our case, 15/1600 represents 15 parts out of a total of 1600 parts.
-
Percentage: A percentage expresses a fraction as a portion of 100. To convert a fraction to a percentage, we divide the numerator by the denominator and multiply by 100. For example, 15/1600 * 100 = 0.9375%.
-
Ratio: A ratio compares two quantities. The ratio of 15 to 1600 can be written as 15:1600 or 15/1600. This shows the relative proportion of one quantity to another.
Calculating the Percentage: 15 out of 1600
Calculating the percentage represented by 15 out of 1600 is straightforward:
-
Divide the numerator by the denominator: 15 ÷ 1600 = 0.009375
-
Multiply the result by 100: 0.009375 × 100 = 0.9375%
Therefore, 15 out of 1600 represents 0.9375%. This can also be expressed as approximately 0.94%.
Interpreting the Result: Context is Key
The significance of 0.94% depends entirely on the context. Let's explore some examples:
-
A Small Percentage in a Large Sample: If we're talking about 15 defective items out of 1600 manufactured, 0.94% might be considered acceptable depending on industry standards and the cost of eliminating defects. This small percentage might represent excellent quality control.
-
A Significant Percentage in a Small Sample: If we're talking about 15 successes out of 1600 attempts in a clinical trial testing a new drug, 0.94% would be considered extremely low and suggest the drug is ineffective. The small sample size is critical.
-
Data Analysis and Statistical Significance: In statistical analysis, a small percentage like 0.94% would need to be carefully evaluated alongside other factors. The statistical significance (whether the result is likely due to chance or a real effect) needs to be determined. Factors like confidence intervals and p-values are essential here.
Real-World Applications: Where 15 out of 1600 Matters
The concept of "15 out of 1600" has implications in numerous fields:
-
Quality Control: In manufacturing, this ratio could represent the percentage of defective products. Companies continuously monitor these figures to maintain quality standards.
-
Medicine and Clinical Trials: As mentioned, in clinical trials, a low success rate might indicate the ineffectiveness of a treatment. Analyzing this data is critical for further research and development.
-
Market Research: In surveys and market research, 15 responses out of 1600 participants representing a specific demographic could indicate a low preference for a particular product or service.
-
Environmental Science: If 15 out of 1600 samples of water show pollution, this suggests a relatively low but potentially concerning level of contamination. Further investigation is necessary.
-
Education: In an exam with 1600 questions, scoring 15 correctly might indicate a significant need for improvement.
-
Finance and Investment: While unlikely to be expressed directly in this format, the underlying principles are used extensively. For example, calculating the percentage of successful investments out of a total portfolio.
Beyond the Numbers: Understanding Probabilities
The statement "15 out of 1600" also opens up discussions about probability. Probability deals with the likelihood of an event occurring. The probability of selecting a defective item from the batch is 15/1600 = 0.009375, or approximately 0.94%.
Advanced Statistical Concepts: Confidence Intervals and P-values
While calculating a simple percentage is useful, a more in-depth statistical analysis is often required for a complete understanding, especially when dealing with sample data. This involves:
-
Confidence Intervals: Confidence intervals provide a range of values within which the true population parameter (e.g., the true percentage of defective items) likely lies. For example, a 95% confidence interval might indicate that the true percentage of defective items is between 0.5% and 1.5%.
-
P-values: P-values measure the probability of obtaining results as extreme as, or more extreme than, the observed results if there were no real effect. A low p-value (typically below 0.05) suggests statistical significance, meaning the observed results are unlikely due to chance alone.
The Importance of Sample Size
The sample size (1600 in this case) is a crucial factor in statistical analysis. A larger sample size generally leads to more accurate and reliable results. With a smaller sample size, a seemingly small percentage like 0.94% could be more susceptible to random variations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do I calculate the percentage increase or decrease if the number changes from 15 to, say, 20 out of 1600?
A: First, calculate the new percentage: 20/1600 * 100 = 1.25%. Then calculate the difference: 1.25% - 0.94% = 0.31%. The percentage increase is 0.31%.
Q: Can this concept be applied to situations with non-numerical data?
A: While the direct calculation of a percentage requires numerical data, the underlying principles of ratios and proportions can be applied to categorical data by creating frequency distributions and then calculating proportions.
Q: What statistical software can I use to perform more advanced analysis on data like this?
A: Several statistical software packages, such as R, SPSS, and SAS, can be used to perform advanced statistical analysis, including calculating confidence intervals and p-values.
Conclusion: The Power of Perspective
The seemingly insignificant fraction of 15 out of 1600, translating to approximately 0.94%, highlights the importance of context in interpreting data. While the percentage itself might seem small, its significance heavily relies on the specific situation. Understanding fractions, percentages, and basic statistical concepts allows for informed decision-making across numerous fields, from manufacturing to medicine to market research. Remember that the numbers alone don't tell the whole story; context, sample size, and more sophisticated statistical methods are crucial for accurate and meaningful interpretations. The journey from a simple fraction to a comprehensive understanding of probability and statistical significance is a powerful example of how seemingly small details can unlock profound insights.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
69 1kg In Stone
Sep 17, 2025
-
94 8kg In Stones
Sep 17, 2025
-
104f To C
Sep 17, 2025
-
360 X 12
Sep 17, 2025
-
20 Off 44
Sep 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 15 Of 1600 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.